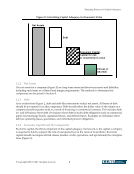
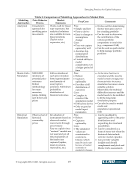
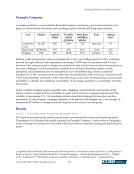
Emerging Practices for Capital Adequacy © Copyright 2003, CCRO. All rights reserved. 45 simple to complex. More complex solutions are likely to require significant analytical resources but provide insights into potential outcomes that are useful to external stakeholders as well as management. Furthermore, total economic capital should decrease as the sophistication of the methodology increases. While this outcome may not always be the case mathematically, simpler methods tend to ignore diversification/correlation effects and thus overestimate risk capital. Market risk and credit loss have been studied sufficiently to determine that, while they are related, there is certainly a diversification benefit that should be captured in the combination. This benefit is lost if one uses the simple sum methodology. These methodologies have been identified as appropriate practices and have been adapted from the experience of financial institutions, insurers, and other practitioners in enterprise risk management and economic capital frameworks. 7.3.1 Simple Sum - Risks Are Assumed to Be Perfectly Correlated The first and easiest method is simply to add the economic capital for market, credit, and operational/operations risk. This is easily accomplished if a consistent confidence level and time horizon have been used in deriving market, credit, and operative risk economic capital. The assumption here is that market, credit, and operative risk have a correlation of one to each other. This method gives an upper bound of economic capital because it assumes that all the worst-case scenarios occur at the same time. 7.3.2 Modern Portfolio Theory - Risks Are Assessed with Estimated Correlation Structure The second method is a variation of the first, where a more explicit correlation structure or matrix is used to combine economic capital. The correlations are measured using historical data of the individual risk components. As a start, we can use the time series of market VaR and credit VaR to estimate historical correlation based on Spearman rank correlation or the exponentially weighted moving average definition. Once economic capital data is available for a long enough period,17 it can be used to calculate the correlation. Given that economic capital is derived from standard deviations, the second step is to use Markowitz’s portfolio theory to determine the total economic capital. MR,OR MR,CR ECOR ECCR ECOR ECMR ECCR ECMR ECOR ECCR ECMR TotalEC 2 2 2 * * 2* * * 2* * * 2* CR,OR + + + + + = MR stands for market risk, CR for credit risk, and OR for operative risk. i,j indicates correlation between two risk components, i and j. One of the key assumptions behind this methodology is the normal distribution of returns. This assumption allows us to use variance as the characterization of total risk. If correlation among risks is less than one, this methodology will show a reduced amount of economic capital required compared with the previous methodology. Thus, an increase in capital adequacy will result. 17 We suggest 3 months minimum.
Purchased by unknown, nofirst nolast From: CCRO Library (library.ccro.org)