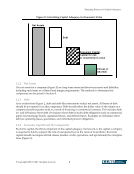
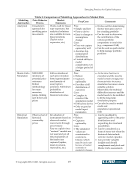
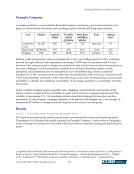
Emerging Practices for Capital Adequacy © Copyright 2003, CCRO. All rights reserved. 17 • Assuming the natural gas price is $3.50, gas prices a month from now can be expected to be between $4.34 and $2.83 (3.50e.214 and 3.50e-.214, where e is the base of natural logarithms or 2.71828) using the monthly volatility at the 95% confidence level. This suggests that gas prices are asymmetric and are expected to move between +84 cents and –67 cents from their current level under an assumed price behavior that follows a lognormal distribution. The range of potential natural gas price outcomes would be between $2.83 and $4.34 per MMBtu. This range of prices would then be applied to the exposure map where a range for financial performance would be estimated and market risk could be calculated. 4.4.2 Monte Carlo Simulation Simulation is an iterative process where the evolution of prices is simulated many times over. Each iteration defines a unique price path over the specified time horizon. The simulation of price evolution needs to jointly simulate volume, weather, and other impacts. This price path is then applied to the exposure map whereupon a distinct financial performance is determined for each increment. Focusing on market risk under the economic capital framework, the process can be diagrammed (Figure 9). Simulation is applicable for modeling stochastic processes in nature, such as the behavior of energy prices over time. There are many complex drivers in estimating energy price movements however, a comparison of the behavior of energy prices may have some or all of the following common features: • The tendency for prices to move around a long-term average (mean reversion) • Seasonal price effects, including weather-related impacts and daily/hourly effects • Volatility levels that move in accordance with the absolute level of price (path-dependent volatility) in a positive or negative relationship • Occasional price spikes • Correlation effects between commodities, geographic regions, and delivery periods across the term structure, which would include basis risk for gas and congestion risk for power.
Purchased by unknown, nofirst nolast From: CCRO Library (library.ccro.org)