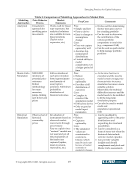
Emerging Practices for Capital Adequacy © Copyright 2003, CCRO. All rights reserved. 33 5.4 Comparison of Credit Risk Models Table 5 provides an overview of various approaches for modeling credit risk. While the table is neither comprehensive nor definitive, it serves as a starting point for understanding the different ways of arriving at a credit risk capital number. The CCRO does not endorse any particular approach and encourages companies to perform their own research to determine what model best suits their needs. Table 5: Overview of Approaches for Modeling Credit Risk Feature Approach Merton-Based Econometric Actuarial Generalized Structural Model Underlying Assumptions Default is function of asset value change - Bottom-up approach Default is function of macroeconomic variables - Bottom-up approach Default is based on buckets of similar size and characteristics - Top-down approach13 Hybrid model using characteristics of the other three models - Bottom-up approach Computational Technique & Performance Simulation with correlation - Slow Analytic with no correlation Simulation – Slow Numerical algorithm - Fast Numerical algorithm - Fast Input Format Counterparty-level records Counterparty-level records Size-based cell totals Rating/size/sub- portfolio cell totals Expected Loss Yes Yes Yes Yes Key Parameters Default rate by rating LGD “Asset” correlations Default rate by rating LGD Macroeconomic variable coefficients Expected loss by exposure bucket Factor loadings Default rate by rating LGD Borrower to factor correlations Unexpected Loss Yes Yes Yes Yes Default Correlation Yes Yes Yes Yes Loss Severity Correlation No No No Yes Nondefault Economic Loss Approach Ratings migration matrix Ratings migration matrix None Changes in future expected loss expectations Default Rate Volatility Yes Yes Yes Yes Economic Capital Yes Yes Yes Yes 13 The actuarial model is referred to as “top-down” because unlike the other three, it stipulates the shape of a distribution for the output and then uses the data to fit the distribution. The other three types allow the distribution to be formed more freely through the calculation process.
Purchased by unknown, nofirst nolast From: CCRO Library (library.ccro.org)