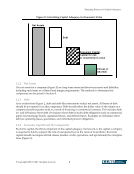
Emerging Practices for Capital Adequacy © Copyright 2003, CCRO. All rights reserved. 30 • Current exposure by counterparty – This measures the organization’s credit exposure to a counterparty. It includes non-negative MTM exposure,11 accounts receivable, unbilled receivables, and adjustments due to netting arrangements and credit enhancements that may be in place. Note that the current exposure is likely to change over time. Thus, for a better assessment of credit risk, companies should look not only at current exposure, but potential future exposure as well. • Potential future exposure by counterparty – This describes how a company’s credit exposure to a counterparty can evolve through time. The PFE is a complex function of many variables that often requires simulation for proper analysis. For example, a deal structure needs to be modeled to track what happens to accounts receivable as deliveries are made over time. Moreover, residual non-negative MTM exposure at each point in time needs to be modeled. This, in turn, requires a price propagation model that describes how forward prices evolve through time. In practice, so many future evaluation dates may prove to be technically cumbersome, but evaluation dates should at least include several future dates that will meaningfully encompass the full maturity of most trades with sufficient frequency to catch any peaks around interim settlement dates. Failure to evaluate PFE with sufficient frequency or horizon length can result in a significant underestimation of exposure. The price propagation model used for this purpose should be identical to that used in measuring market risk and should reflect intertemporal, intercommodity, and basis correlations. Finally, counterparty netting and margining arrangements need to be accounted for in the calculation. • Exposure by counterparty – This summarizes how much the organization could lose prior to any recovery in case the counterparty defaults. It is based on the current and PFE calculations. Figure 16 is a stylized exposure graph. 11 Maximum of zero or MTM this has the effect of eliminating all the negative MTM value and resembles in form the mathematics of a call option. This may complicate and skew the distribution of MTM exposure, rendering the usual normality assumptions dubious.
Purchased by unknown, nofirst nolast From: CCRO Library (library.ccro.org)