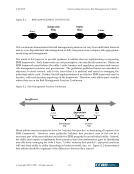
4/20/2020 Understanding Enterprise Risk Management for Utilities © Copyright 2007, CCRO. All rights reserved. 29 3. Implementation of Framework ERM implementations should be highly customized at each firm such that the final framework is appropriate and reflects the complexity, size and sophistication of the company. Nevertheless, there are several key ingredients to a successful ERM framework and there are specific steps that can be taken to facilitate implementation. 3.1. Six Steps to Implementation Virtually all ERM applications follow a typical framework as described in this section of the report. This process is illustrated in the following chart and each step is subsequently described. Examples of items to consider in each step are also shown. 3.1.1. Identify and Quantify Risks The first step to an effective ERM framework is to identify and quantify the risks of the business. There are several techniques used by companies to inventory and quantify the risks. Once a firm identifies the dozens of risks they face, the risks are typically categorized and prioritized based The Six Step Process for Enterprise Risk Management 1. Identify and Quantify Risks •Market Risk •Credit Risk •Operations Risk •Operational Risk •Business Risk 2. Establish Risk Tolerance and Policies •Corporate Strategy and Risk Management Objectives •ERM and Governance Policy •Authority and Sanctions Policies •Credit Policy •Financial Policy •Hedge Policy •Safety Policy 3. Establish Business Unit Strategies and Metrics •Market/Speculative/Hedging Strategies and Metrics •Credit Strategy and Metrics •Financial Strategy and Metrics •Safety Strategy and Metrics •Internal Risk Management Approval of Strategy 5. Execute Strategies •Examples Include: •Commodity Trading •Credit Risk Mitigation •Preventative Maintenance •Safety Program •Organizational Coordination 6. Monitor Risk and Reporting •Are There New Risks? •Any Necessary Changes to Policies or Strategies? •Is Corporate Strategy Yielding Expected Results? •Policy Compliance •Value at Risk •Rates at Risk •Financial Results •Results Vs. Performance Metrics 4. Implement Controls and Procedures •Trading Controls •Business Unit Procedures •Internal Risk Mgt. Committee •Independent Risk Oversight Begin/ Continue The Six Step Process for Enterprise Risk Management 1. Identify and Quantify Risks • Market Risk • Credit Risk • Operations Risk • Operational Risk • Business Risk 2. Establish Risk Tolerance and Policies • Corporate Strategy and Risk Management Objectives • ERM and Governance Policy • Authority and Sanctions Policies • Credit Policy • Financial Policy • Hedge Policy • Safety Policy 3. Establish Business Unit Strategies and Metrics • Market/Speculative/Hedging Strategies and Metrics • Credit Strategy and Metrics • Financial Strategy and Metrics • Safety Strategy and Metrics • Internal Risk Management Approval of Strategy 5. Execute Strategies • Examples Include: • Commodity Trading • Credit Risk Mitigation • Preventative Maintenance • Safety Program • Organizational Coordination 6. Monitor Risk and Reporting • Are There New Risks? • Any Necessary Changes to Policies or Strategies? • Is Corporate Strategy Yielding Expected Results? • Policy Compliance • Value at Risk • Rates at Risk • Financial Results • Results Vs. Performance Metrics 4. Implement Controls and Procedures • Trading Controls • Business Unit Procedures • Internal Risk Mgt. Committee • Independent Risk Oversight Begin/ Continue
Purchased by unknown, nofirst nolast From: CCRO Library (library.ccro.org)