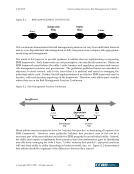
4/20/2020 Understanding Enterprise Risk Management for Utilities © Copyright 2007, CCRO. All rights reserved. 4 1.2. What is ERM? The CCRO has defined ERM as the program or process enacted to identify, assess, quantify and respond to the complete set of risks facing a firm in an integrated fashion. The CCRO emphasized that Enterprise Risk Metrics are a key component of an ERM framework and enable the assessment, quantification and reporting of identifiable risks. The utility considering the implementation of an ERM framework can view it as the aspirational destination on a Risk Management Continuum (see Figure 1.2). On all parts of the continuum, the traditional activities associated with identifying, assessing, quantifying, controlling and mitigating specific market, credit, operative or business risks will exist.2 The main differentiator across the spectrum lies in the level of integration achieved in the firm. Figure 1.2: RISK MANAGEMENT CONTINUUM On the left end of the continuum lies the silo approach to risk management in which all risks are more or less treated on a stand-alone basis with little consideration given to portfolio level interactions. This fragmented approach may even translate into different approaches to measuring the same type of risk across business units or at different points in time. The next step in the continuum is to “Integrated Silos”, where firms exhibit greater levels of risk management capability and there is consistency with which risks are measured within a risk or organizational silo (e.g., all supplier and customer credit risk is measure and monitored consistently across the utility). The next step of the continuum marks a clear progression toward an ERM framework, whereby risks from different silos (e.g., distribution, transmission and generation) are consistently assessed, managed and reported in an integrated manner. At the far end of the continuum is ERM which represents the highest level of sophistication currently possible for an organization. Such a framework helps a company deal effectively with uncertainty by providing a portfolio view of the risks affecting the organization across all silos, and thus enables a common understanding of risk. At this level, the business units continue to be involved in the identification, assessment, qualification and quantification, control and mitigation of risk. As such, the basic building blocks for managing the different silos continue to be useful, but ERM is layered over them and leverages the information to provide an integrated perspective and bring the risks to the attention of the appropriate and cross-organizational management level. 2 Earlier white papers provide a comprehensive discussion of what the CCRO members consider “best practice” in several of these areas such as Analytics and Valuation, Credit Risk Management, Governance and others. Readers interested in reviewing these documents can find them at www.ccro.org. Silos Multi- Silos ERM Integrated Silos
Purchased by unknown, nofirst nolast From: CCRO Library (library.ccro.org)