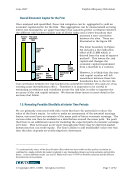
June 2007 Capital Adequacy Extension © Copyright 2007, CCRO. All rights reserved. Page 90 of 92 hedging guidelines that governed its open exposures at any point in time there were no VaR limits in place. The CRO thought that by evaluating different VaR trading limits vs. the hedging guidelines, the company could potentially hedge away this new risk. Besides a reduction in default rate, management also wanted to understand the financial liquidity impact from potential margin calls created by implementing a trading VaR. The company’s hedging activities are one-sided in that hedges are placed to lock in supply prices after customers are signed up therefore, a lower VaR would force the company to increase its hedging activities and would carry the potential of increasing its collateral outlays for margin requirements. To monitor the liquidity liability created by reducing the VaR limits, they created a margin call liability metric which represents the average margin call for a VaR strategy. Table 2 looks at different VaR limits and the associated default rates and margin call liabilities. Table 2 VaR Limit Default Rate Margin Call Liability No VaR Limit 6.25% $78MM $100MM 5.65% $81MM $75MM 5.30% $85MM $50MM 4.35% $109MM While EMTCo management liked the default rate reduction at the $50MM VaR limit, they were concerned about the 40% increase in the margin call liability (vs. no VaR limit). They selected the $75MM VaR limit because it met their default rate reduction goal while only increasing their liquidity liability by 9%. EMTCo. Management felt that this VaR strategy provides a good balance between financial liquidity and economic value. 10.2.10. Conclusion This application focuses on demonstrating some of the key objectives of Capital Adequacy primarily creating a framework that assesses the viability of a firm’s business plans and evaluates actions and opportunities through: • A better and more comprehensive understanding of the firm’s risk • Utilize a forward looking RAROC metric to not only optimize the firm’s allocation of capital but also to improve the pricing of risk and corresponding risk/return measures • Utilize a backward looking RAROC to determine risk neutral returns in order to monitor performance and encourage the creation of future economic value • Demonstrating the trade-off between financial liquidity and economic value in respect of evaluating business opportunities Our illustrated methodology overcomes one of the major obstacles presented in the original Capital Adequacy paper the inability to realistically extend the risk horizon because of the dynamic modeling issues created by management intervention. Utilizing the enabling technology of agent-based modeling has allowed us to mimic management’s
Purchased by unknown, nofirst nolast From: CCRO Library (library.ccro.org)