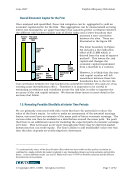
June 2007 Capital Adequacy Extension © Copyright 2007, CCRO. All rights reserved. Page 51 of 92 losses from default.18 Subsequent sections of this paper will look at why this assumption is not entirely valid however, for the practical example below, the one year default probability for a counterparty is determined assuming that the premium is the entire compensation for assuming this default risk. In order to directly compare a bond to its equivalent maturity Treasury instrument to yield the true spread, we need to determine the zero-coupon yield of the corporate and government bond. Comparing zero-coupon yields removes the distortion that coupon payments will have on the yield, thereby creating an ‘apples-to-apples’ comparison. The zero coupon yield can be computed using the “boot-strap: method, where the zero- rate is implied from the discounted coupon payments and principal.19 See Insert 5.1 for an example of this method. 18 Options, Futures, and Other Derivatives. 4th Edition. John C. Hull. Prentice Hall Inc. 2000. 19 Options, Futures, and Other Derivatives. 4th Edition. John C. Hull. Prentice Hall Inc. 2000.
Purchased by unknown, nofirst nolast From: CCRO Library (library.ccro.org)