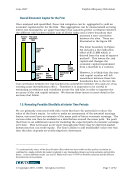
June 2007 Capital Adequacy Extension © Copyright 2007, CCRO. All rights reserved. Page 59 of 92 • Foreign exchange rates, government expenditures • The aggregate savings rate As the economy gets worse, the rate of defaults and credit downgrades accelerates, and as the economy does better, there are consequently fewer defaults and credit downgrades. This type of relationship can be translated into the default probability and credit migration analysis by tying the above listed factors to the specific situation of the company being analyzed. The country, industry, and industry sector should be considered as each category is affected by the economy in differing ways. This is particularly true for energy companies, as the nature of the business is very cyclical and highly correlated to macroeconomic factors. 5.10. Current and Potential Future Exposures The determination of the current exposure is comparatively straight forward as it entails aggregating the total positive MTM exposure with any accounts receivable and/or unbilled receivables. The challenge comes in calculating the Potential Future Exposure (PFE). This is where Market Risk has a direct impact and the risk measurement techniques used in measuring Market Risk can be deployed here to determine the maximum potential exposure. Because of this interconnectedness with Market Risk, it is prudent to execute market and credit analysis simultaneously to ensure coordinated timeframes, price levels, etc. This concept will be discussed further in Chapter 5, the Market Risk Chapter. In determining potential future exposure, it is helpful to think of credit exposure as a portfolio of elements whose value changes with movements in market rates. Figure 5.4 graphically demonstrates how this concept is executed. Figure 5.4 Determination of Potential Future Exposure
Purchased by unknown, nofirst nolast From: CCRO Library (library.ccro.org)