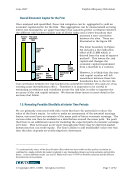
June 2007 Capital Adequacy Extension © Copyright 2007, CCRO. All rights reserved. Page 56 of 92 Among the aspects that add complexity to this approach are: • Off-balance sheet structures will not be reflected in the value of the assets unless the user obtains the value of these structures and incorporates them into the equation.24 • A company will typically have many forms of debt with differing maturities and seniority levels. • Assets such as Goodwill will not add to the value of assets in liquidation scenarios. These types of assets must be considered when modeling asset value.25 • The Merton Model, like Black-Scholes, assumes a lognormal distribution of the potential value of the assets. This assumption may not be indicative of the real world. 5.6. Default Rate Volatilities and Correlations Even when good estimates of the EDP’s are used, uncertainty exists about whether or not a counterparty will ultimately default. Default volatility captures the fact that default either does occur or does not and reflects the fact that actual default rates could differ from expectations. Table 5.2, which encompasses data from 1970 though 1996, demonstrates that the standard deviation around actual default rates can be quite high, denoting wide variability in actual default rates. Default correlations measure the likelihood of multiple simultaneous defaults. Idiosyncratic default risk results from the random chance that any single counterparty will go into default over the one-year time horizon because of conditions specific to that counterparty. Systematic default risk results from the chance of experiencing many defaults due to prevailing economic conditions. A common practice is to infer correlations among defaults from equity prices. Each obligor is assigned to an industry and geographical sector. Correlations are then inferred from co-movements of the equity prices relative to common risk factors. 24 Energy Modeling. Credit Risk Management for the Energy Industry – Some Perspectives. V. Kaminsky, V. Shanbhogue. Risk Books. 2005. pg. 346. 25 Ibid. Table 5.2 One Year Default Rates (%) Credit Rating Default Rate Standard Deviation Aaa 0.00 0.0 Aa 0.03 0.1 A 0.01 0.0 Baa 0.12 0.3 Ba 1.36 1.3 B 7.27 5.1
Purchased by unknown, nofirst nolast From: CCRO Library (library.ccro.org)