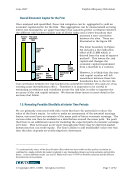
June 2007 Capital Adequacy Extension © Copyright 2007, CCRO. All rights reserved. Page 88 of 92 The next step is to calculate the expected or average change in value of the investment from the default scenarios. CEQi represents the amount of equity needed to support the investment to maintain a 5.25% firm default probability over a 5 year horizon. If the value of the investment is highly correlated to the firm’s value during stressful scenarios, the investment will require a higher amount of equity. If the value of the investment is not well correlated to the firm’s value during stressful scenarios and the firm’s portfolio can diversify most of the investment’s loss, the investment’s CEQ or the equity required to support the investment will be low. A negatively correlated investment will show an increase in value at default. Thus CEQi represents the diversified risk or equity requirement of investment i in the firm’s portfolio. To illustrate this decomposition approach, we will take one of the contracts on EMTCo.’s books and determine its return on incremental equity. Contract #31 has an initial MTM value of $5.248 million. Using the default scenarios, we can calculate its expected realized plus unrealized value at default to be a $0.325 million loss. The steps in calculating this value are as follows: 1. Calculate the contract’s realized value at default- discount the contract’s cash flows generated before the default period back to the present. 2. Calculate the contract’s unrealized value at default - discount the contract’s MtM at the default period back to the present. 3. Calculate the contract’s total value at default – add the contract’s unrealized value and realized value together. 4. Calculate the delta value - subtract the contract’s total value from its initial MtM value. This resulting value represents the contract’s change in value from its initial value to its value at default. Once these steps have been performed for each default scenario then calculate the contract’s CEQi by summing the delta values for each default scenario and then divide by the number of default scenarios. Thus the required equity or CEQi to support this contract is $5.573 million (or $5.248 million - -$0.325 million). We will calculate its economic value created by charging the investment for its required equity. Using the same capital utilization rate as the incremental example, the capital charge is: Capital Charge = $5.573 million * rate (7%, 5 years) = $2.243 million Thus the economic value created by the investment, where economic value created represents the value created with a risk neutral default probability, is $3.0 million ($5.248 million – $2.243 million) and the return on incremental equity or RAROC is 53% over 5 years ($3.0 million / $5.573 million) for an annualized return of 9%. If the true return on this contract falls below the firm’s hurdle rate, the firm may have undervalued the contract’s risk in its price. By utilizing the calculated RAROC metric on new contracts, the firm will have a better understanding of the investment’s true return/risk to the firm and be better suited to price its risk. Thus this firm can use this method to not only improve its risk price strategy but also to allocate capital based on
Purchased by unknown, nofirst nolast From: CCRO Library (library.ccro.org)