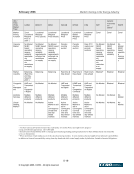
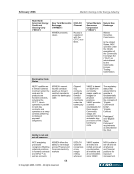
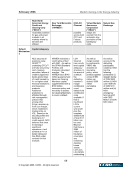
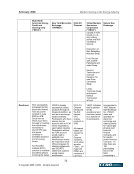
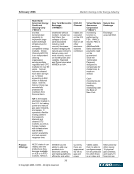
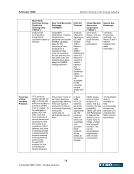
February 2006 Market Clearing in the Energy Industry 5-17 5. KEY STAKEHOLDER PERSPECTIVES: CURRENT POSITIONS AND ISSUES As shown previously, market clearing may provide significant benefits to energy markets in the form of reduced risks, lower collateral requirements, increased liquidity, and greater transparency. These overall benefits, however, are not necessarily distributed evenly among market participants and each constituency has a view on the use and effectiveness of market clearing based on its particular circumstance and situation. The purpose of this section is to describe the perspectives of market clearing for key stakeholders, including: ISO/RTOs, merchants, load serving entities, trading organizations, and regulators. 5.1. Independent System Operators (ISOs) and Regional Transmission Operators (RTOs) ISOs and RTOs4 in North America are non-profit organizations and public utilities subject to FERC, state (i.e., ERCOT is subject to Public Utility Commission of Texas (PUCT) jurisdiction), or Provincial Energy Board jurisdiction that are, at a minimum, responsible for maintaining system reliability and NERC security, coordination and planning of the transmission system of their region. ISO/RTOs provide independently managed and non-discriminatory access for physical power transmission, administer commercial use of service in their region, and in many cases provide an integrated marketplace for energy market products, which may include physical energy (real-time and/or day-ahead markets), ancillary services, financial products such as financial transmission rights and virtual and capacity markets. ISOs and RTOs, therefore, are natural aggregators of credit risk in the form of accounts receivable and could benefit from credit risk mitigation. Each markets’ participants provide for the mutual credit underwriting of the market (or, in many cases, multiple markets5) as a whole. (Note that ERCOT is based on load ratio share, not full loss mutualization to all participants.) All of the ISO/RTOs recognize the importance of performing credit risk management. However, differences can be significant in the way ISO/RTOs administer their respective markets to manage credit risk and these regional differences have been identified by the ISOs /RTOs as a challenge to credit risk mitigation solutions. 5.1.1. Current status In operation of their respective markets, ISO/RTOs provide functions associated with market clearing. These functions may include the ability to net purchases and sales (of like transactions, or across different products, both financial and/or physical), and providing a master settlement bill with individual line items. As the ISO/RTO marketplace expands, both in the number of markets that have become ISO/RTOs and in the number of products provided in these markets, ISO/RTOs realize the growing 4 RTOs are similar in operation and concept to ISO’s however, one distinct feature is that RTOs are fully independent from market participants. 5 A single company may be a market participant in all ISO/RTO markets, and transact bilaterally under multiple Open Access Transmission Tariffs (OATT).
Purchased by unknown, nofirst nolast From: CCRO Library (library.ccro.org)