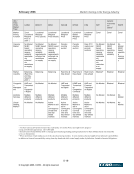
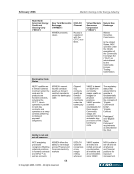
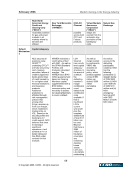
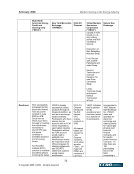
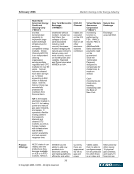
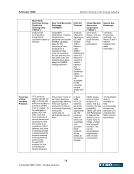
February 2006 Market Clearing in the Energy Industry 3-12 © Copyright 2006, CCRO. All rights reserved. rated counterparties. There is greater flexibility in the credit arrangements in a two-tier model. In a two-tier model, the clearing members (i.e., FCMs) are often highly rated financial institutions. FCMs, being in the business of extending credit to corporate entities, can then customize this service, achieving a financial solution tailored to the needs of each participant. Often, the credit extended by an FCM to a corporate client is just one part of a larger, overall credit commitment to that customer. In a two-tier system, collateral is netted only among the customers of the FCM. All things being equal, a single tier model nets more efficiently for customers because all collateral is netted in a single pool. In addition, the single-tier model has the advantages of cost and transparency. There are fewer middlemen in the single-tier model and this can reduce the total fees and charges associated with clearing a transaction. But, of course, the single tier model is based on mutualized risk. 3.4. Clearing in financial markets The financial markets in North America, Europe and Asia-Pacific have been served by well- developed clearing infrastructures for decades. Different geographies have different institutional arrangements: in some European and Asian markets many exchanges will have a dedicated clearinghouse in an arrangement similar to the NYMEX clearing arrangement. In other markets there is a highly centralized clearinghouse that clears and settles transactions across many asset classes and markets. The Depository Trust Clearing Corporation (DTCC) is the central clearinghouse for the entire North American financial markets. It clears and settles: • Equity securities traded on the NYSE, Amex and NASDAQ and other exchanges • Corporate bonds traded in the over-the-counter (OTC) market • Mortgage-backed securities traded in the OTC market • Government securities traded in the inter-dealer and OTC market In Europe for many years banking institutions filled the roles that the DTCC plays in North America: central depository and central counterparty. Now, Euroclear and Clearstream provide depository, clearing and settlement services on a centralized basis. Euroclear serves 25 equity markets and 30 bond markets in 80 countries. Clearstream, a unit of Deutsch Börse Group, serves markets in Germany, Luxemburg and other countries. Two main trends have driven the structure of clearinghouse services in the financial markets: the drive toward broader and deeper netting pools and the extension of services that replace multiple, redundant trade processing operations within clearinghouse customers with a single utility. • The trend toward broader and deeper netting pools is illustrated by the DTCC. It represents the merger of the Government Securities Clearing Corporation, the Mortgage-Backed Securities Corporation, Fixed-Income Clearing Corporation and the National Securities Clearing Corporation. By consolidating these formerly independent clearinghouses, clients can cross-margin across asset classes and achieve dramatically more efficient collateral utilization.
Purchased by unknown, nofirst nolast From: CCRO Library (library.ccro.org)