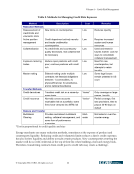
Volume 4— Credit Risk Management © Copyright 2002, CCRO. All rights reserved. 19 • Exposure analysis by counterparty family, tenor • Exposure trend analysis and limit concentrations (by industry, region, ultimate parent, commodity product, risk grade) • Aging of receivables • Deals approved with exceptions • New counterparty/limit approved: last 30 days by business by SIC, limit amount and risk rating • Watch list/counterparties within X percentage or dollar amount of established limits • Limit violations/excesses • Trending of limits exceptions by exposure and units (number of deals and counterparties) based on business, commodity, SIC, etc. • Trends: Excess limit by risk rating • Trading halted Common Counterparty A fundamental cornerstone of credit risk management is the ability to capture accurate and reliable counterparty hierarchy information (parent/subsidiary relationships). • Counterparty data inventory/maintenance report by ultimate parent • Counterparty agreement inventory • Counterparty exception report: Incomplete identifying information, number of days from previous review Analytical Tools/Reserves General reports used to manage key performance indictors include: • Credit memorandum (the basis for the risk rating and limit assigned) • Financial statement exception report • Risk rating/change and credit score exception reports • Estimated default frequency (EDF) change summary • Reserve and capital adequacy Credit Infrastructure • Deals pending approval • Deals approved, not documented • Deals approved/declined by product, analyst, etc.
Purchased by unknown, nofirst nolast From: CCRO Library (library.ccro.org)