Financial Liquidity Risk Management for Energy Industry Market Participants
© Copyright 2025, CCRO. All rights reserved. 4
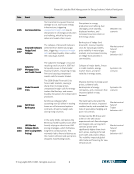
Date Event Description Impacts Drivers
2005 Hurricane Katrina
Hurricane Katrina caused massive
damage to U.S. Gulf Coast energy
infrastructure, triggering
unexpected margin calls due to
disruptions in oil and gas production
and refining, which led to price
spikes and supply chain issues.
Disruptions in energy
production and refining, fuel
shortages, price volatility,
displaced workers, and
increased insurance claims in
the energy sector.
Weather risk
scenario
2006-
2007
Amaranth Advisors
Hedge Fund
Collapse
The collapse of Amaranth Advisors
stemmed from failed natural gas
bets, triggering unexpected margin
calls and deep liquidity strain within
the natural gas market.
Bankruptcy of hedge fund
Amaranth, massive liquidity
crisis for natural gas traders,
price volatility in natural gas
markets, and increased scrutiny
on hedge fund activities in
commodities.
Market control
failure?
Trader
behavior risk?
2007
Subprime
Mortgage Crisis
and Credit Crunch
The subprime mortgage crisis and
resulting credit crunch in 2007 led
to liquidity issues in the broader
financial markets, impacting energy
firms and causing unexpected
margin calls for energy traders.
Collapse of major banks, freeze
in credit markets, energy
market losses, and price
volatility in energy assets.
Systemic risk
scenario
2008 Global Financial
Crisis
The 2008 Global Financial Crisis
froze credit markets, causing a
sharp drop in energy prices,
unexpected margin calls for energy
traders like Barclays, and severe
liquidity disruptions for independent
producers.
Massive declines in energy asset
prices, collateral calls,
bankruptcies of energy
companies, and a recession that
impacted global energy
demand.
Systemic risk
scenario
2008 SemGroup
Bankruptcy
SemGroup collapsed after
sustaining over $3 billion in trading
losses on oil futures and options
contracts, driven by margin calls
during rising oil prices.
The bankruptcy disrupted the
midstream oil sector, impacted
creditor banks, and revealed the
risks of speculative hedging and
poor risk controls.
Market control
failure?
Trader
behavior risk?
2010-
2015
LNG Market
Collapse (Short-
term vs Long-term
Pricing)
In the early 2010s, companies like
BG Group faced liquidity issues after
heavily relying on short-term LNG
pricing strategies, which fell below
long-term contract prices. This
mismatch led to financial distress as
the market softened and spot prices
dropped, exacerbating losses.
Companies like BG Group and
others in the LNG sector
experienced cash flow shortages
and margin calls, as long-term
contract prices were
significantly higher than short-
term prices, leading to forced
asset sales and project delays.
The volatility impacted global
LNG trade and financing for new
infrastructure.
Market control
failure?
Trader
behavior risk?
© Copyright 2025, CCRO. All rights reserved. 4
Date Event Description Impacts Drivers
2005 Hurricane Katrina
Hurricane Katrina caused massive
damage to U.S. Gulf Coast energy
infrastructure, triggering
unexpected margin calls due to
disruptions in oil and gas production
and refining, which led to price
spikes and supply chain issues.
Disruptions in energy
production and refining, fuel
shortages, price volatility,
displaced workers, and
increased insurance claims in
the energy sector.
Weather risk
scenario
2006-
2007
Amaranth Advisors
Hedge Fund
Collapse
The collapse of Amaranth Advisors
stemmed from failed natural gas
bets, triggering unexpected margin
calls and deep liquidity strain within
the natural gas market.
Bankruptcy of hedge fund
Amaranth, massive liquidity
crisis for natural gas traders,
price volatility in natural gas
markets, and increased scrutiny
on hedge fund activities in
commodities.
Market control
failure?
Trader
behavior risk?
2007
Subprime
Mortgage Crisis
and Credit Crunch
The subprime mortgage crisis and
resulting credit crunch in 2007 led
to liquidity issues in the broader
financial markets, impacting energy
firms and causing unexpected
margin calls for energy traders.
Collapse of major banks, freeze
in credit markets, energy
market losses, and price
volatility in energy assets.
Systemic risk
scenario
2008 Global Financial
Crisis
The 2008 Global Financial Crisis
froze credit markets, causing a
sharp drop in energy prices,
unexpected margin calls for energy
traders like Barclays, and severe
liquidity disruptions for independent
producers.
Massive declines in energy asset
prices, collateral calls,
bankruptcies of energy
companies, and a recession that
impacted global energy
demand.
Systemic risk
scenario
2008 SemGroup
Bankruptcy
SemGroup collapsed after
sustaining over $3 billion in trading
losses on oil futures and options
contracts, driven by margin calls
during rising oil prices.
The bankruptcy disrupted the
midstream oil sector, impacted
creditor banks, and revealed the
risks of speculative hedging and
poor risk controls.
Market control
failure?
Trader
behavior risk?
2010-
2015
LNG Market
Collapse (Short-
term vs Long-term
Pricing)
In the early 2010s, companies like
BG Group faced liquidity issues after
heavily relying on short-term LNG
pricing strategies, which fell below
long-term contract prices. This
mismatch led to financial distress as
the market softened and spot prices
dropped, exacerbating losses.
Companies like BG Group and
others in the LNG sector
experienced cash flow shortages
and margin calls, as long-term
contract prices were
significantly higher than short-
term prices, leading to forced
asset sales and project delays.
The volatility impacted global
LNG trade and financing for new
infrastructure.
Market control
failure?
Trader
behavior risk?